Actualidad
Wax and Melatonin Preserve Pineapple Postharvest Quality
Treatment with wax and melatonin helps maintain the postharvest quality of pineapple by stabilizing cell wall integrity and mitigating oxidative stress

Pineapple (Ananas comosus L., family Bromeliaceae) is one of the most widely traded tropical fruits globally. However, it faces various postharvest quality challenges, including internal browning, chilling injury, and pathogen infections.
Browning typically begins in the core of the fruit and progressively spreads to the flesh, turning it a dark brownish color. This leads to deterioration, decay, and a significant loss of commercial value.
Numerous recent studies have focused on preventing internal browning in pineapple, exploring treatments such as calcium chloride, abscisic acid, modified atmosphere packaging, heat treatment, and wax coating.
Wax Application
Wax has been widely used to mitigate postharvest stress and disease in various horticultural crops, including apples, mangoes, and citrus fruits.
Studies have shown that postharvest treatment of pineapple with wax can reduce organic acid content, delay discoloration and ripening, and improve overall fruit quality.
When applied in combination with other bioregulators, wax can produce a synergistic effect, effectively enhancing postharvest quality, extending shelf life, and reducing spoilage during storage.
Effects of Melatonin
Melatonin is a multifunctional hormone that can reduce respiration rate, decay, and softening, thereby maintaining overall fruit quality.
It also acts as a powerful free radical scavenger and enhances resistance to both abiotic and biotic stress.
Melatonin delays senescence by decreasing ethylene synthesis, activating antioxidant enzymes, and reducing the browning index.
Pineapple Studies
In a recent study, postharvest treatments with wax, melatonin, and a MIX (wax + melatonin) were applied to pineapples. A transcriptomic analysis was then conducted to explore the molecular mechanisms behind delayed fruit senescence induced by these substances.
Positive Results from MIX (Wax + Melatonin) Treatment
The results showed that the MIX treatment significantly delayed ripening and preserved pineapple quality by reducing browning, minimizing weight loss, maintaining fruit firmness, and decreasing oxidative stress.
Transcriptomic analysis following MIX application revealed a large number of differentially expressed genes, primarily associated with amino sugar and nucleotide metabolism, cell wall formation pathways, phenylpropanoid biosynthesis, and glutathione metabolism (a powerful antioxidant tripeptide).
Furthermore, the MIX treatment was found to induce the expression of numerous transcription factors that activate genes related to antioxidant defense mechanisms, disease resistance, and cell wall degradation resistance.
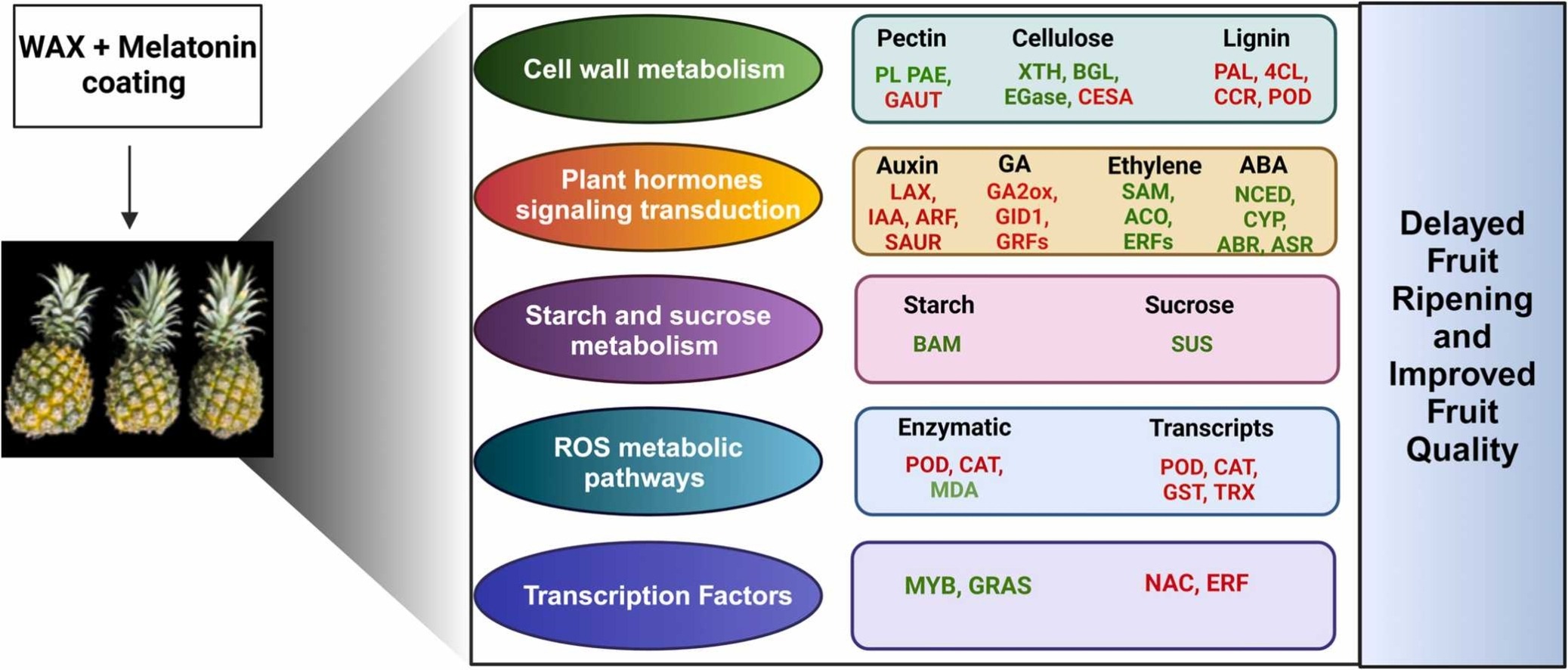
Graphical abstract Rahman et al., 2025
Sources
Rahman, F. U.; Qiu, J.; Lei, Q.; Chen, W.; Li, X.; Zhu, X. (2025).
The effect of wax and melatonin combined treatment on pineapple fruit ripening and key regulating factors revealed by transcriptome analysis
Postharvest Biology and Technology, 227: 113578.
Picture
https://wikifarmer.com/library/pt-br/article/colheita-manuseio-armazenamento-e-venda-de-abacaxi Acceso el 05/05/2025.













